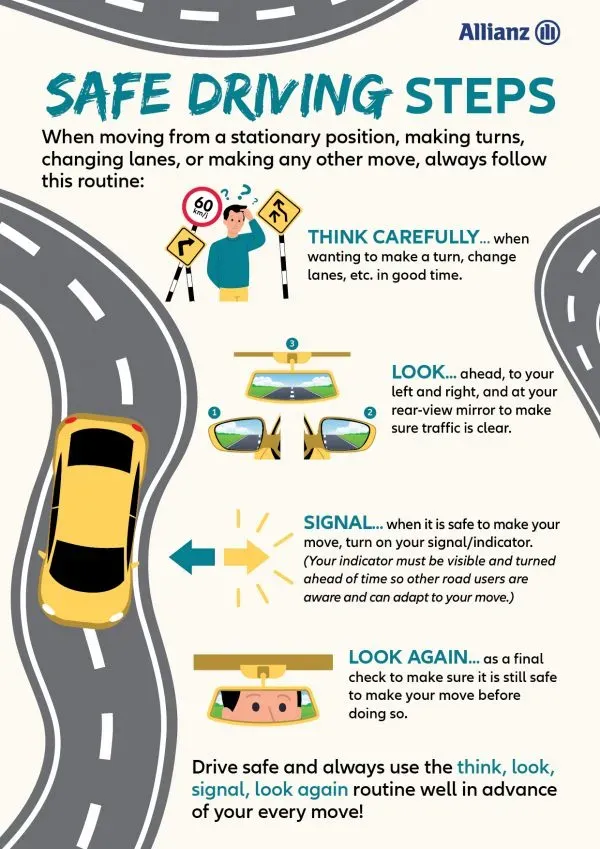
Safe driving in the modern automobile has evolved from a purely hands-on skill to a collaborative effort between the driver and a suite of safety technologies. In today’s vehicles, advanced systems work behind the scenes to prevent accidents, reduce injury, and assist you in making better decisions on the road, powered by modern car safety features. This article introduces the core ideas behind driver assistance systems and vehicle safety technology that elevate your awareness and control. Whether you are a new driver or an experienced motorist, understanding these technologies will help you stay safer, more confident, and more in control during every journey. To make the most of your driving experience, combine these features with safe driving tips with new cars and practiced habits.
Viewed through a broader lens, contemporary road safety becomes a network of terms like driver support technologies, intelligent safety systems, and proactive protection tools rather than a single device. From adaptive cruise control and automatic braking to lane-keeping assistance and blind-spot monitoring, these concepts describe a cohesive safety ecosystem that works in harmony with the driver. Understanding this ecosystem helps motorists optimize settings, adjust habits, and stay alert as vehicles anticipate dangers. As technology evolves, the emphasis shifts toward predictive safety and seamless human–machine collaboration, preserving personal responsibility while enhancing protection. By embracing these ideas alongside steady attention and prudent choices, you can navigate today’s roads more confidently and safely.
Safe driving in the modern automobile: Integrating driver assistance systems and core safety features for smarter journeys
Safe driving in the modern automobile relies on a collaborative mix of human judgment and advanced vehicle safety technology. Modern cars combine anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and traction control with airbags and reinforced crash structures to reduce injury and preserve control during emergencies. In practice, these core safety features act as a safety net that supports your decisions, especially when attention lapses occur or road conditions are challenging. By understanding how each element works in concert with driver assistance systems, you can navigate twists, curves, and adverse weather with greater confidence and resilience.
To make the most of these capabilities, drivers should view the technology as a supplement rather than a substitute for safe habits. The emphasis on redundancy—where active safety features and ADAS cooperate to prevent or mitigate incidents—means you should stay engaged, monitor road conditions, and be prepared to intervene when necessary. Maintaining clean sensors, updating software when prompted, and following manufacturer guidance are practical steps that keep the system performing as intended and maximize the benefits of modern car safety features, vehicle safety technology, and safe driving overall.
Safe driving in the modern automobile: Practical use, customization, and ongoing awareness to enhance safety
A practical approach to safe driving involves customizing ADAS and related safety tools to suit your driving style and typical road conditions. Features like Adaptive Cruise Control, Lane Keeping Assist, Automatic Emergency Braking, and Blind-Spot Monitoring can be tuned for more conservative or more responsive behavior. Understanding where automation ends and human judgment begins helps you leverage these tools without becoming overly dependent on them. In this way, driver assistance systems enhance your situational awareness while you maintain core skills—scanning ahead, signaling early, and adjusting speed to traffic and weather.
Ongoing awareness is essential because no system is flawless. ADAS can be challenged by faded lane markings, heavy rain, or glare, and sensors must be kept clean and correctly calibrated. Regular maintenance, timely software updates, and sensor checks support reliable performance of vehicle safety technology. For drivers seeking practical guidance, remember to keep following distances appropriate, use reminders and alerts as cues—not as guarantees—and consult the owner’s manual or a qualified technician if you notice unusual system behavior. This mindful approach aligns with safe driving tips with new cars and ensures you stay in control while benefiting from modern safety innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do modern car safety features and driver assistance systems enhance safe driving in the modern automobile?
Safe driving in the modern automobile is supported by a spectrum of systems that augment but do not replace driver judgment. Core features like ABS, ESC, and traction control help prevent skids, while airbags and crumple zones protect occupants. Driver assistance systems—Adaptive Cruise Control, Lane Keeping Assist, Automatic Emergency Braking, Blind-Spot Monitoring, and 360-degree cameras—provide warnings and, in some cases, intervention, but they still require you to stay alert and ready to take control. Remember to keep sensors clean, consult the owner’s manual for setup, and avoid overreliance on technology.
What are practical safe driving tips with new cars to maximize vehicle safety technology and driver assistance systems?
To maximize safe driving tips with new cars, start by learning your vehicle’s safety feature roster and practicing in a safe area before relying on ADAS in traffic. Regularly clean sensors and keep software up to date; adjust following distance and steering assist to your conditions. Use ADAS as a support, not a replacement for hands-on driving; stay attentive to road signs, lane markings, and weather, and be prepared to intervene. Finally, maintain the vehicle (tires, brakes, suspension) to keep your vehicle safety technology functioning as intended.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Core safety features | ABS prevents wheel lock during hard braking; ESC and traction control detect loss of steering or tire grip and apply brakes selectively while adjusting engine power. Airbags, seat belts, and crumple zones work with these systems to minimize injury. These features are designed to augment safe driving habits, creating a safety net that activates when you need it most. |
| Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) | Adaptive Cruise Control maintains a safe following distance; Lane Keeping Assist gently steers you back if you drift; Automatic Emergency Braking detects an imminent collision and applies brakes if you don’t respond. Blind-Spot Monitoring and Rear Cross-Traffic Alert warn you about hidden vehicles; Parking Assist and 360-degree cameras help prevent low-speed collisions. |
| Redundancy and safety net | Multiple features provide overlapping protection. One feature may nudge or steer, while another can fully brake in critical moments. This redundancy improves safety when you remain engaged and ready to take control. |
| Limitations and driver role | No system is flawless; ADAS can be affected by poor road markings, heavy rain, fog, or unexpected obstacles. Driver attention and judgment remain crucial. Stay familiar with manuals, update software when prompted, and keep sensors clean and calibrated. |
| Active vs Passive safety | Passive safety includes structure, airbags, and seat design to protect occupants in a crash. Active safety refers to systems that help you avoid a crash (ABS, ESC, AEB, and ADAS). |
| Practical usage and customization | Customize settings to suit driving style and conditions; calibrate sensors and keep software updated. Clean sensors regularly and adjust following distance and steering assist as needed. |
| Environment and situational awareness | Weather, lighting, road geometry, and traffic patterns influence feature engagement. Understand how features behave in different conditions and respond to warnings or corrective actions accordingly. |
| Driver habits and safety culture | Maintain safe following distance, scan the road, use indicators, and avoid distractions. Regular maintenance supports feature performance and reinforces defensive driving. |
Summary
Safe driving in the modern automobile combines human judgment with intelligent safety features to create safer journeys on today’s roads. Core systems like ABS, ESC, airbags, and seat belts form a protective backbone, while ADAS such as Adaptive Cruise Control, Lane Keeping Assist, Automatic Emergency Braking, and blind-spot monitoring provide guidance and automated assistance. The driver remains central; redundancy among safety features offers a safety net, but no system replaces vigilance and good driving habits. Practical steps—keeping sensors clean, updating software, calibrating cameras, and tailoring ADAS settings to conditions—help maximize safety. Understanding active versus passive safety clarifies how each element contributes to prevention and protection. Environment and road conditions influence feature behavior, so stay attentive, anticipate actions, and respond promptly when warnings occur. By blending responsible driving with modern safety technology, you reduce risk and increase predictability for yourself and others on the road. The future of safe driving in the modern automobile lies in ongoing education, diligent maintenance, and thoughtful use of vehicle safety technology, ensuring safer journeys today and tomorrow.