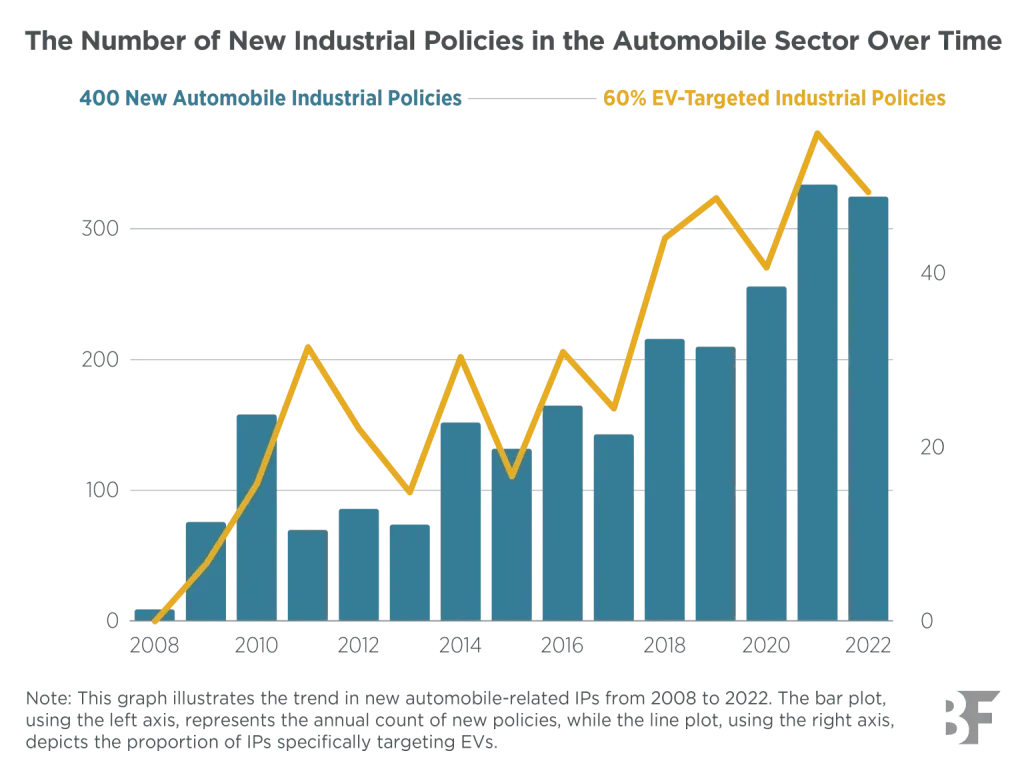
Policy shapes the automobile industry in profound and lasting ways. Understanding policy effects on the automobile industry helps explain why governments deploy incentives and standards to steer investment and innovation. Emissions standards and automotive regulation push automakers toward cleaner propulsion, safer designs, and more efficient production. Incentives and standards in automotive policy can tilt the economics of new platforms, batteries, and charging networks, shaping which technologies scale first. For brands, suppliers, and consumers, the balance of auto industry incentives and standards helps determine costs, timing, and technology choices.
From a regulatory perspective, government rules, subsidies, and governance shape how cars are designed, manufactured, and marketed. The broader governance framework includes emissions controls, safety mandates, data privacy, and infrastructure policy that steer technological choices. By viewing the industry as an ecosystem driven by policy levers and market signals, analysts can better anticipate investment cycles and supply chain shifts. In this framing, industry regulation, environmental targets, and incentive programs work together to influence costs, competition, and consumer access.
Policy shapes the automobile industry: Incentives and standards as levers of innovation and investment
Policy shapes the automobile industry in profound and lasting ways, guiding where investment flows and which technologies become mainstream. When policymakers implement incentives and set standards, they influence the economics of electric vehicles, battery technology, and charging infrastructure. This dynamic illustrates incentives and standards in automotive policy in action as governments tilt market outcomes toward cleaner, safer, and smarter mobility.
To maximize positive outcomes, policy designers favor glide paths that gradually phase out subsidies as technologies mature, preserving predictability for automakers’ capital plans. Abrupt shifts in incentives can disrupt supply chains and create price volatility for consumers. Understanding policy effects on the automobile industry helps stakeholders evaluate how incentives align with broader goals like energy security, emissions reduction, and domestic job creation.
Emissions standards and automotive regulation: Driving innovation across the global auto market
Emissions standards push automakers to invest in cleaner propulsion, higher energy efficiency, and advanced battery technology, reshaping product portfolios and manufacturing footprints. These standards also influence supplier ecosystems, R&D priorities, and the pace of electrification and decarbonization across regions.
Regulatory harmonization across the United States, European Union, and Asia reduces compliance friction and helps suppliers scale globally. The interplay between automotive regulation and incentives—embodied by concepts like auto industry incentives and standards—can accelerate adoption when designed with predictable timelines, transparent testing, and balanced cost burdens.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do incentives and standards in automotive policy shape the policy effects on the automobile industry?
Incentives and standards in automotive policy steer where capital flows, accelerating electrification, battery tech, and charging infrastructure. They create a predictable glide path for automakers and suppliers, helping plan capital expenditure and product timelines, while shaping the overall policy effects on the automobile industry.
How do emissions standards and automotive industry regulation influence innovation, costs, and consumer outcomes in the auto sector?
Emissions standards drive cleaner propulsion and energy efficiency, and automotive industry regulation governs safety, data privacy, and recalls. Together, they spur R&D and new partnerships, can raise production costs, and affect consumer adoption—especially when standards are harmonized across regions to reduce compliance friction.
| Policy Focus | Key Points | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Incentives | Governments use tax credits, subsidies, and R&D support to steer investment toward electrification, propulsion, and charging infrastructure. | Accelerates capital expenditure, shifts technology adoption, and affects timing/scale of rollout. |
| Standards | Emissions and safety standards push cleaner propulsion, battery tech, and ADAS adoption; harmonization reduces compliance friction. | Drives R&D, supply chain diversification, and collaboration; can raise costs if misaligned. |
| Regulation & Market Structure | Vehicle labeling, warranties, recalls, and data privacy for connected cars influence product design and risk management; cybersecurity and data governance matter. | Improves consumer information and product quality; shapes data governance and risk management. |
| Equity, Trade & Global Competition | Tariffs, local-content rules, and regional incentives influence where factories are built and supplier priorities. | Shifts investment across regions; supports regional EV supply chains and job creation. |
| Policy Effects Across Regions | US: incentives + fuel economy rules; EU: decarbonization push; China: subsidies and local manufacturing mandates. | Leads to regional shifts in investment, skills, and product portfolios; cross-border alignment matters. |
| Balancing Incentives & Standards | Need predictable phase-outs; balance carrots and sticks; engage stakeholders to avoid distortions. | Improves forecastability and innovation while reducing risks of misalignment. |
| Future Trends | Decarbonization, energy security, resilience; recycling targets; lifecycle emissions accounting; data governance for connected/autonomous vehicles. | Policy evolves toward holistic sustainability and smarter mobility, shaping tech roadmaps. |
Summary
Policy shapes the automobile industry by guiding investment, technology choices, and consumer options in an interconnected policy landscape. In this context, incentives, standards, and regulation drive innovation, influence costs and timelines, and determine how quickly cleaner, smarter vehicles reach customers. Stakeholders—from automakers to suppliers to regulators—must navigate these levers to balance growth with safety, reliability, and environmental goals.