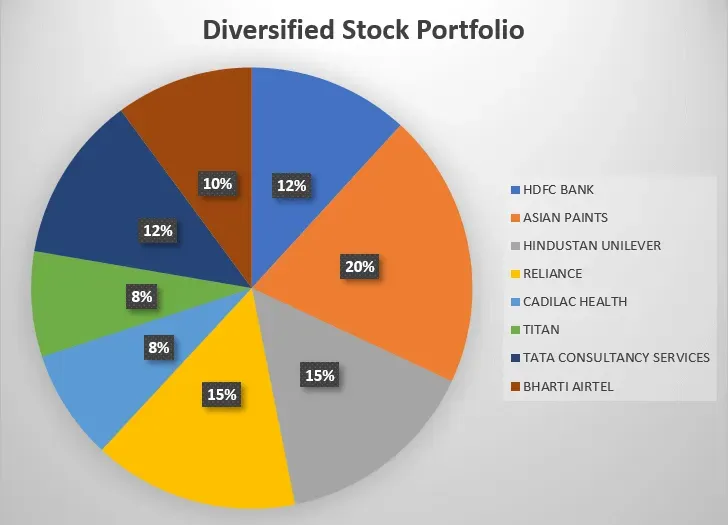
A diversified stock market portfolio isn’t a luxury for seasoned investors; it is a sensible strategy for reducing risk while pursuing sustainable growth across different market environments, economic cycles, and time horizons, and it helps you stay adaptable when unexpected shocks hit. In an era of rapid market shifts, stock market diversification across asset classes, geographies, sectors, and investment styles helps you weather volatility, capture a wider set of growth opportunities, reduce drawdowns during downturns, and improve your odds of meeting long-term financial goals. This holistic approach aligns with portfolio diversification strategies and asset allocation strategies, balancing potential upside with disciplined risk controls, tax efficiency, liquidity considerations, and cost awareness that compound over the long run, while emphasizing cross-asset resilience and the subtle interactions among stocks, bonds, real assets, and alternatives. By thoughtfully selecting a core mix and implementing a disciplined rebalancing process, you maintain steady allocation discipline, incorporate new ideas without surrendering your base exposure, and stay aligned with your time horizon, personal risk tolerance, tax considerations, and ongoing cost controls. Whether you are new to investing or refining an existing plan, the framework emphasizes repeatable steps, ongoing monitoring, and tax-efficient opportunities that preserve upside while managing downside risk through diverse market regimes, planning horizons, and disciplined behavioral habits.
Think of it as a multi-asset investment approach that blends equities, fixed income, real assets, and alternatives to reduce dependence on any single market. Instead of chasing the hottest stock, focus on a resilient allocation that spreads risk across regions, company sizes, and investment styles, creating steadier performance through diverse drivers. This broader view leverages cross-asset diversification, disciplined asset allocation, and risk budgeting to support sustainable growth through varying economic cycles. Practically, you’ll construct a core portfolio with broad-market exposure and add satellite positions that enhance diversification without overconcentration, then rebalance periodically. By framing diversification in terms of risk control, cost efficiency, and long-term objectives, you align your strategy with how informed investors evaluate success beyond pinpoint stock picking.
Diversified Stock Market Portfolio: Core Principles and Asset Allocation Strategies
Building a diversified stock market portfolio begins with clarity about goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. By spreading exposure across geographies, market caps, and asset classes, investors reduce reliance on a single driver of return and improve the chances for smoother performance across market cycles. This approach aligns with asset allocation strategies that balance growth, income, and stability while emphasizing stock market diversification as a core discipline.
In practice, the framework emphasizes core and satellite positions, disciplined rebalancing, and cost awareness. The core provides broad market exposure while satellites add targeted tilts or hedges, enabling a resilient diversified stock market portfolio without excessive turnover. Ongoing monitoring of correlations, volatility, and fees helps ensure that diversification remains effective and aligned with risk management in investing.
Asset allocation strategies guide how much to allocate across equities, fixed income, and alternatives, with diversification guiding the choice of geographies and sectors. This approach also supports portfolio diversification strategies by encouraging a repeatable process for adjusting allocations as markets shift and as personal circumstances change.
Portfolio Diversification Strategies: Implementing Risk Management in Investing with Cost-Effective Exposure
Portfolio diversification strategies are most effective when anchored in risk management in investing rather than chasing recent performance. A well constructed plan distributes risk through multiple assets that do not move in lockstep, reducing drawdowns and preserving upside potential during market stress. This stance relies on diversification across asset classes, regions, and investment styles to build resilience.
To implement cost efficient exposure, focus on low cost index funds and carefully select bond or ETF products that minimize fees and tax inefficiencies. Regularly review correlations and drawdown history to ensure the portfolio remains aligned with your risk tolerance, time horizon, and goals. This ongoing process embodies risk management in investing as a practical discipline rather than a one time exercise.
Additionally, rebalancing cadence and tax aware strategies help maintain the intended balance between growth and stability. By applying disciplined asset allocation strategies and monitoring diversification metrics, investors can stay on course even as markets evolve. This reinforces the value of diversification as a long term habit rather than a reaction to new headlines.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a diversified stock market portfolio and why is stock market diversification important for long-term investing?
A diversified stock market portfolio spreads risk across geographies, sectors, and asset classes to reduce the impact of any single downturn. By applying stock market diversification with thoughtful asset allocation strategies, investors can smooth returns, manage risk in investing, and pursue sustainable growth aligned with their time horizon and risk tolerance. Regular monitoring and a disciplined rebalancing plan help preserve the diversification you rely on.
What practical steps form a framework for building a diversified stock market portfolio using asset allocation strategies?
Start by clarifying your objectives and risk tolerance; establish a risk-aware asset allocation; build core and satellite positions; prioritize cost efficiency and tax planning; set a disciplined rebalancing plan; monitor diversification metrics and risk indicators; and adapt to life changes. This practical framework follows portfolio diversification strategies and risk management in investing to help you maintain a resilient, cost-efficient diversified stock market portfolio over time.
| Key Idea | Summary |
|---|---|
| Purpose of diversification | Reduces risk, smooths volatility, and aligns with time horizon and risk tolerance. |
| Core building blocks | Core equity exposure by geography, international diversification, fixed income ballast, real assets, low-cost vehicles, and a rebalancing framework. |
| Framework steps | Clarify objectives; establish risk-aware asset allocation; build core & satellite positions; prioritize costs and taxes; set a disciplined rebalancing plan; monitor diversification metrics; adapt to life changes. |
| Core vs Satellite | Core holdings are broad-market, long-term exposures; satellites add tilt, opportunities, or hedges without compromising core diversification. |
| Rebalancing | Use a regular cadence and drift thresholds to maintain target allocations and manage risk. |
| Monitoring metrics | Asset correlations, portfolio standard deviation, drawdowns; optional beta, Sharpe ratio, and downside capture. |
| Costs and tax efficiency | Favor low-cost ETFs and tax-efficient funds; consider asset location to optimize after-tax returns. |
| Practical allocation example | Core ~60–70% (US large-cap, international, emerging, small-cap tilt); Satellite ~20–30%; Fixed income ~20–30%. |
| Common mistakes | Overconcentration, neglecting international diversification, market timing, ignoring costs, poorly defined goals and lack of rebalancing. |
Summary
A concise overview of the base content distilled into key points and a practical framework for building and maintaining a diversified stock market portfolio.