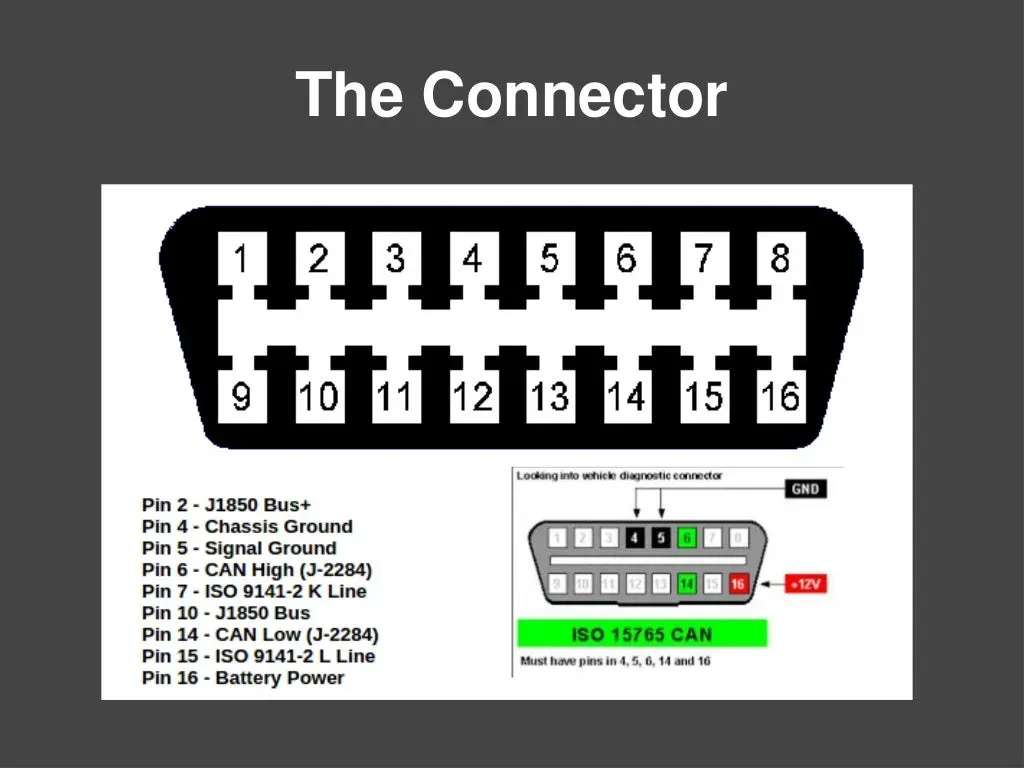
CAN Bus and OBD-II explained: ADAS, in-car connectivity
CAN Bus and OBD-II explained provides a clear doorway into how modern vehicles’ electronic networks operate, framing a landscape where dozens of sensors, controllers, actuators, and user devices exchange data continuously without a single central host, so that everything from fuel injection timing to seat positioning can be coordinated in real time, while this integrated communication also reveals why software updates can alter behavior and why understanding these networks matters to drivers and engineers alike.To appreciate the mechanics, consider CAN bus protocol basics: messages are structured into frames with identifiers that indicate priority and content, arbitration rules resolve simultaneous transmissions, and checksums verify integrity, ensuring that critical data—such as braking signals or throttle position—arrives with minimal latency while hundreds of other messages coexist on the same network.