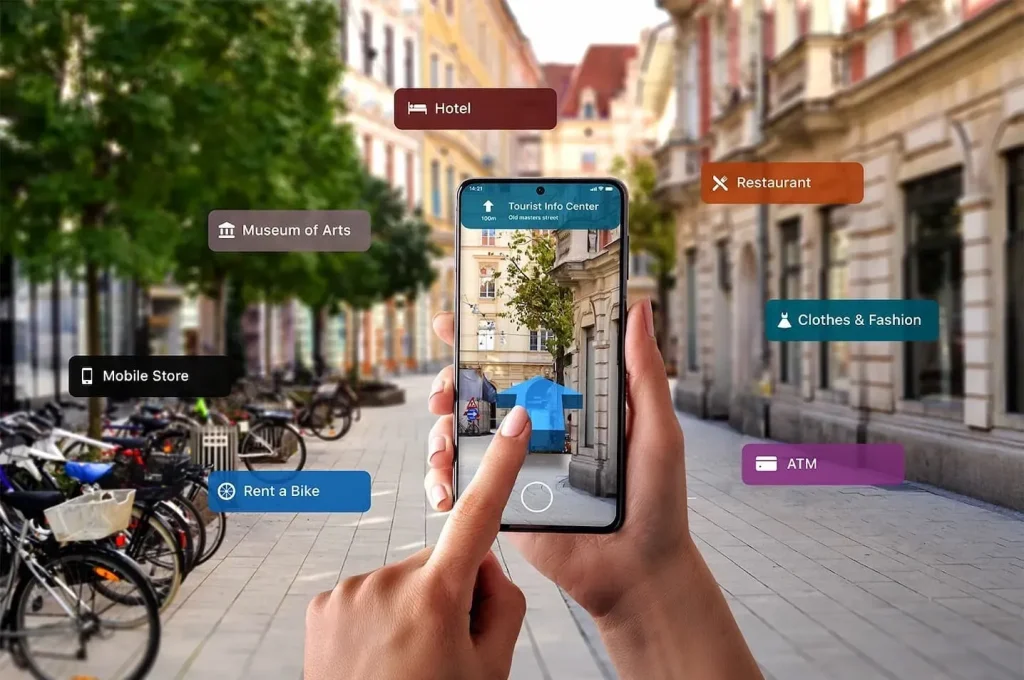
Augmented Reality reshapes how we perceive our surroundings by layering digital information onto the real world. This technology acts as a practical bridge between physical spaces and digital insights, transforming learning, work, and everyday tasks. As the field continues to mature, it complements existing platforms and influences how we design experiences that are context-aware. Overlays deliver just-in-time guidance without distracting from the surrounding environment. This overview examines what the technology can do, how it differs from other digital layers, and why it is increasingly shaping applications across industries.
Beyond one device or app, this field sits on the broader spectrum of spatial computing, where digital overlays align with the real world to guide decisions. Businesses are exploring how the layered information can support hands-on training, remote assistance, and on-site problem solving. Similar concepts live in the realm of mixed reality and other immersive technologies, bridging the gap between perception and action. As organizations adopt AR technologies and related tools, the focus shifts toward scalable content, data security, and measurable outcomes. These trends echo virtual experiences, data overlays, and context-aware guidance that align with industry adoption.
Augmented Reality in Practice: AR Technologies, AR Applications, and the Enterprise Advantage
Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto the real world, anchored by AR technologies such as real-time computer vision, depth sensing, and spatial mapping. Devices—from smartphones to light, wearable glasses—carry the sensors and processing power needed to anchor virtual objects to physical space, while software platforms handle asset rendering, occlusion, lighting, and interaction. Cloud-enabled delivery and collaboration extend the reach of AR experiences, letting teams access up-to-date content without burdening local hardware. This blend of perception, processing, and presentation is what makes AR technologies practical—not just futuristic—across industries with AR applications ranging from field service to education and retail.
In enterprise settings, AR applications empower technicians on the shop floor, healthcare teams in the operating room, and field engineers in the field to access contextual data exactly where decisions are made. The real value emerges when AR complements other realities—MR for persistent, layered collaboration and VR trends that drive immersive training and prototyping—creating a cohesive toolkit rather than isolated experiments. As 5G, edge computing, and AI mature, AR experiences become more fluid, secure, and scalable, enabling faster onboarding, safer operations, and richer customer interactions.
Coordinating AR with Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality for Scalable, Immersive Solutions
AR sits along a spectrum that includes Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality. VR delivers fully immersive environments, while AR augments the real world with contextual digital layers, and MR enables natural, persistent interactions that blend both. In practice, enterprises deploy AR for on-site guidance and MR for collaborative planning, sometimes pairing AR overlays with VR headsets to support parallel training tracks. This cross-pollination aligns with VR trends toward richer, more capable experiences and leverages AR technologies to keep humans meaningfully engaged in real environments.
To harness this spectrum effectively, organizations should adopt a blended strategy anchored by measurable use cases, robust governance, and interoperable platforms. Start with pilots that quantify improvements in productivity, safety, and customer engagement, then scale through standardized AR applications and MR-enabled workflows. Partnerships with hardware manufacturers, software developers, and standards bodies help reduce fragmentation, while cloud-enabled content delivery ensures that AR, VR, and MR tools stay synchronized across devices and locations. In this way, the integration of AR with Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality becomes a unified approach to learning, design, and operational excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Augmented Reality (AR) differ from Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR) in real-world business applications?
AR overlays digital content onto the real world, preserving awareness of surroundings and enabling on-site guidance and product visualization. VR creates fully immersive, synthetic environments for hands-on training and prototyping away from the real world. Mixed Reality bridges the two by enabling natural, persistent interactions with digital content in real space, supporting collaborative design and remote planning. Understanding this spectrum helps organizations tailor AR-enabled workflows across industries and leverage MR and VR where appropriate.
What are the core AR technologies powering AR applications, and how do they deliver real-time overlays in the real world?
AR technologies combine computer vision, depth sensing, and sensor fusion (cameras, depth sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, GPS) to detect surfaces, track motion, and anchor virtual content to physical space. Spatial mapping (SLAM) maintains stable anchors as you move, while rendering with realistic lighting and occlusion makes overlays appear seamless. Cloud and edge computing provide assets and collaboration capabilities, and fast networks keep AR applications responsive with real-time updates.
| Focus | |
|---|---|
| What AR is | Overlays digital content onto the real world to enrich perception without replacing it; enables context-aware, real-time information at points of decision and in various settings. |
| AR vs VR vs MR | AR augments existing reality; VR creates fully synthetic environments; MR blends digital content with the real world for more natural interactions. Enterprises often deploy AR and MR together for layered experiences. |
| Building blocks & technologies | Computer vision, depth sensing, sensors (cameras, accelerometers, gyroscopes, GPS); real-time rendering with occlusion and lighting; spatial mapping/SLAM; cloud for asset delivery and collaboration. |
| Industry applications | Retail/Marketing, Manufacturing/Maintenance, Healthcare, Education/Training, Logistics/Field Service; AR improves engagement, accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration in each domain. |
| AR advantages | Productivity gains, safety improvements, enhanced customer engagement; benefits amplified by 5G, edge computing, and AI for scalable, secure experiences. |
| Challenges | Hardware constraints (battery, comfort, display brightness, field of view); content creation bottlenecks; privacy and data protection; accessibility considerations. |
| Path to maturity | Governance, robust security, and impact measurement; pilot with concrete use cases; partnerships across hardware, software, and standards to reduce fragmentation. |
| Future outlook | Wearables become more capable; smarter AI-driven content; deeper integration with enterprise software; hybrid AR/VR experiences across business and consumer contexts. |
Summary
HTML table above summarizes the core concepts of Augmented Reality from the provided content.