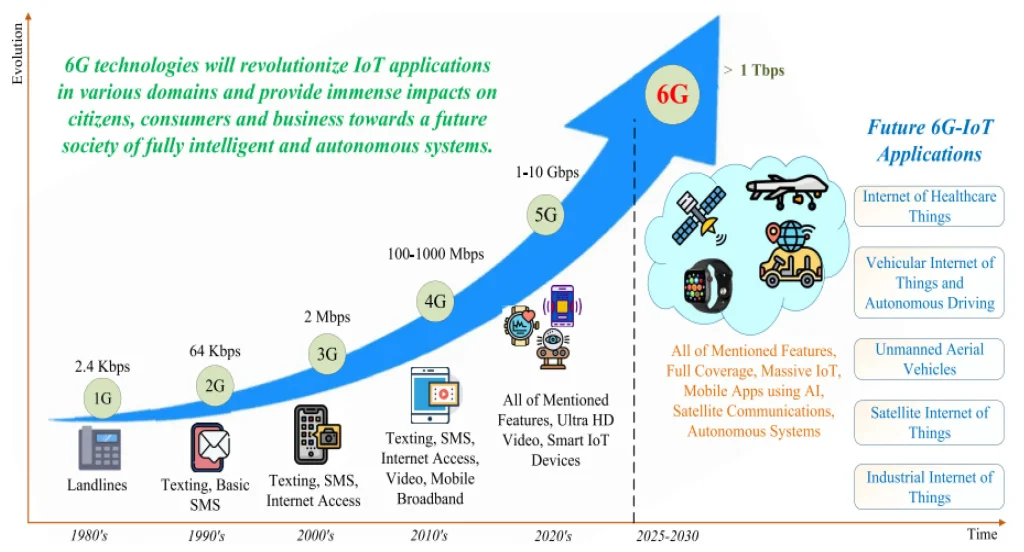
IoT to 6G marks the next frontier in how we design, deploy, and scale digital ecosystems. From the early days of connected devices to today’s multi-sense networks, this evolution blends edge computing, AI in telecommunications, and resilient security to unlock smarter operations. This transition drives smarter cities, efficient industries, and safer daily life by enabling context-aware services and near real-time analytics. Optimizing for ultra-reliable connectivity and low latency, organizations should map their data pipelines to edge and cloud resources, preparing for architectures that support holographic communications and massive device densities. In short, the IoT evolution is setting the stage for a future where networks, devices, and AI work in concert to deliver secure, context-rich experiences.
Viewed through a broader lens, this transition is the convergence of sensor networks with ultra-fast wireless platforms and network intelligence. It is the move from simple device connectivity to intelligent networks where edge processing and autonomous automation unlock new business models. This framing aligns with the growth of digital twins, smart infrastructure, and data-driven operations supported by cloud-to-edge architectures. Together, these terms describe the same trajectory—the shift toward reliable, scalable systems where devices, networks, and analytics collaborate to transform industries and cities.
IoT to 6G: Enabling Edge-Centric, Context-Aware Networks
From the IoT evolution to 6G technology, we are witnessing a move from basic sensor data to intelligent, context-aware ecosystems. Edge computing brings processing closer to devices, slashing latency, reducing backhaul traffic, and enabling AI in telecommunications to optimize networks in real time. In smart cities, this architecture supports adaptive traffic management, environmental sensing, and safer public services through near-instant decision cycles.
For industries, 6G connectivity unlocks holographic communications, massive device densities, and autonomous operations. Planning for IoT to 6G means building interoperable platforms, robust security, and data governance that keep sensitive information close to the source while still enabling cloud-scale analytics. The result is improved reliability, faster time-to-insight, and new service models across manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and city-scale deployments.
Strategies for a Resilient IoT Evolution: Edge, Security, and Standards
To realize the IoT evolution in practice, enterprises should adopt scalable edge computing platforms, decide which data stays at the edge versus what moves to the cloud, and implement network slicing and SDN to prioritize critical applications such as telemedicine and emergency services. This approach reduces data movement costs while preserving privacy and enabling rapid analytics closer to where data is generated. As 6G technology matures, edge-enabled analytics and AI at the edge will further shrink decision times, strengthening the role of AI in telecommunications.
Security, privacy, and interoperability are foundational. Embracing open standards and interoperable ecosystems helps devices from different vendors work together at scale, supporting smart cities and industrial IoT while reducing vendor lock-in. By aligning governance, data handling, and zero-trust security with edge and cloud capabilities, organizations can unlock sustainable value from the IoT evolution as networks advance toward 6G.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the IoT evolution shape the transition to 6G technology and edge computing for smart cities?
The IoT evolution has driven dense sensor networks and diverse device types, generating data at scale. 6G technology offers ultra-high speeds, sub-millisecond latency, and AI-powered networks. Edge computing processes data near the source, reducing backhaul loads and enabling real-time analytics for smart city applications such as traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety. By combining IoT evolution with 6G and edge computing, organizations can deploy context-aware services that preserve privacy and scale across urban environments, supported by AI in telecommunications for continuous optimization.
What role does AI in telecommunications play in bridging IoT and 6G for industrial use cases?
AI in telecommunications enables self-optimizing networks, predictive maintenance, and dynamic resource allocation at the edge, accelerating IoT insights as we move toward 6G. In industrial use cases, this supports digital twins, real-time monitoring, and autonomous operations in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. Edge computing keeps sensitive data local, improving latency and privacy while 6G technology expands scale and reliability for enterprise deployments.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | IoT to 6G marks a turning point in how we design, deploy, and scale digital ecosystems; the goal is not only faster speeds but smarter, safer, and more autonomous systems with seamless connectivity, context awareness, and deep integration with AI and edge computing. |
| The IoT Foundation and Its Evolution | From isolated devices to industrial and consumer IoT; requires robust connectivity, standardized data formats, and secure protocols; edge computing emerges to reduce latency, bandwidth costs, and enable autonomous, context-aware services at scale. |
| What 6G Brings to the Table | Multi-gigabit speeds, sub-millisecond latency, and near-perfect reliability; supports AI at the network edge; intelligent autonomous networks; enables massive device densities; emphasizes energy efficiency and security. |
| From IoT to 6G: Industry Impacts | Manufacturing: real-time monitoring and digital twins; Smart cities: large-scale sensor networks with edge analytics; Healthcare: telemedicine and robotic-assisted procedures; Logistics & agriculture gain smarter routing and real-time visibility; improved consumer experiences due to low latency and stability. |
| Key Enabling Technologies | Edge computing brings intelligence closer to devices; AI at edge and cloud enables insights, automation, and optimized network usage; 6G infrastructure includes advanced spectrum management, Terahertz bands, dense deployments, and SDN; network slicing; strong security and interoperability. |
| Challenges & Opportunities | Spectrum availability and management; Terahertz engineering challenges; energy efficiency; data governance and privacy; opportunities include tactile internet, immersive AR, autonomous systems, and new revenue streams with resilient operations. |
| Practical Roadmap for Enterprises | Define a clear data strategy; invest in scalable edge compute platforms and interoperable IoT gateways; run pilots in high-impact areas (smart buildings, manufacturing, asset tracking); embed security at every layer; partner with network providers and standards bodies to stay ahead of 6G specs. |
| Future Outlook and Conclusion | The path from IoT to 6G is about intelligent, context-aware networks that can support billions of devices, deliver AI-driven insights at the edge, and enable real-time, ultra-reliable connectivity. Expect smarter cities, more resilient supply chains, and personalized healthcare as core outcomes; embracing this evolution today positions organizations to thrive in the IoT to 6G era. |
Summary
IoT to 6G marks the dawn of a new era in connected technology. This evolution will shape ecosystems where devices, networks, and intelligence converge to deliver ubiquitous, context-aware experiences with AI-enabled decision making at the edge. As multi-gigabit speeds meet near-instantaneous latency and pervasive security, industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities will become more autonomous, resilient, and efficient. To capitalize on these opportunities, organizations should start with a clear data strategy, invest in scalable edge infrastructure and interoperable gateways, and partner with standards bodies to align with evolving 6G specifications. In this descriptive journey from IoT to 6G, connectivity becomes a strategic asset that accelerates innovation across every sector, enabling smarter operations, better user experiences, and a more secure, connected world.